And send traffic to remote wireshark.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless-mobility/80211/200527-Fundamentals-of-802-11-Wireless-Sniffing.html#anc12
Wireshark Capture filter - host 10.1.1.3 more info
1) WLC / AP side
Here are the steps in order to collect a trace using a sniffer mode LAP
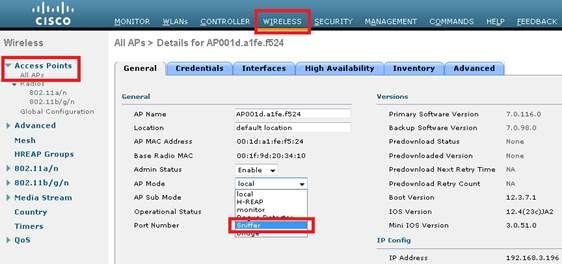
- Configure the AP in Sniffer mode:
The AP will reboot and it will not be able to serve clients.
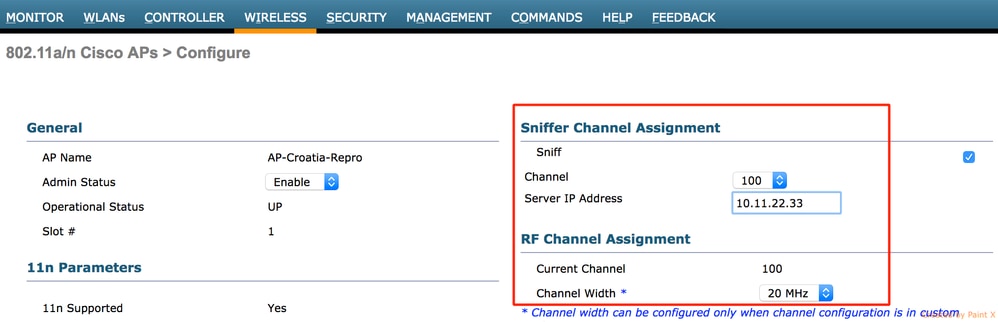
- Once the AP has re-joined the WLC, configure the radio of the AP (802.11b/g/n or 802.11a/n):
- specify the sniffer IP address
- select the channel
- enable sniffing
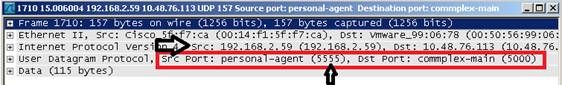
- The sniffer will receive the 802.11 traffic encapsulated using the airopeek protocol, from the WLC management IP address with source port UDP/5555 and destination UDP/5000
2) Sniffer side: Wireshark
If using Wireskark to receive the traffic, follow the steps below:
- Set the capture options to receive only traffic coming from the sniffing AP. If you set the filter only for port UDP 5000, you will miss IP fragments in the capture if the AP has to fragment the packet (which will happen if it sniffed a 1500 bytes long frame to which it needs to add PEEKREMOTE encapsulation):
This filter is optional but strongly recommended as it excludes all the non-wireless related traffic from the capture. Consider that the WLC sends traffic to a UDP port there’s no application listening on the sniffer side; this results in having a ICMP port-unreachable response for each packet received from the WLC.
Although this is expected, the filter above helps to exclude also this traffic which is useless and so it can only cause the trace to be bigger and more difficult to read.
- Then, start the capture:
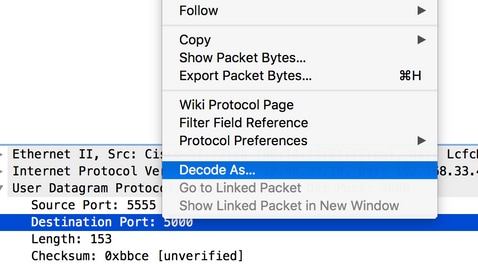
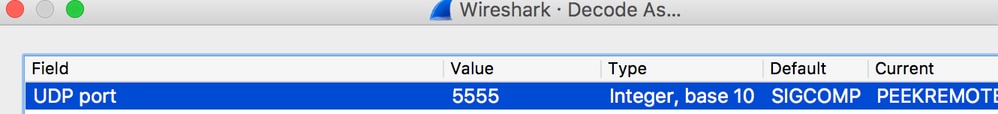
- The captured traffic has to be “decoded as..” PEEKREMOTE in order to be able to see the 802.11 traffic:
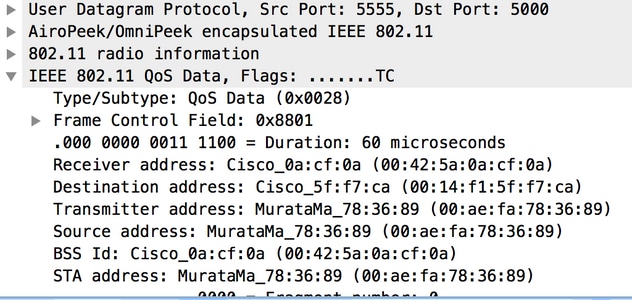
- The 802.11 traffic will now be visible:
The RF info shown above (e.g. the channel, signal strength, noise..) are added by the AP.